Next: Miniature Circuit Breaker Symbols in Electrical Diagrams

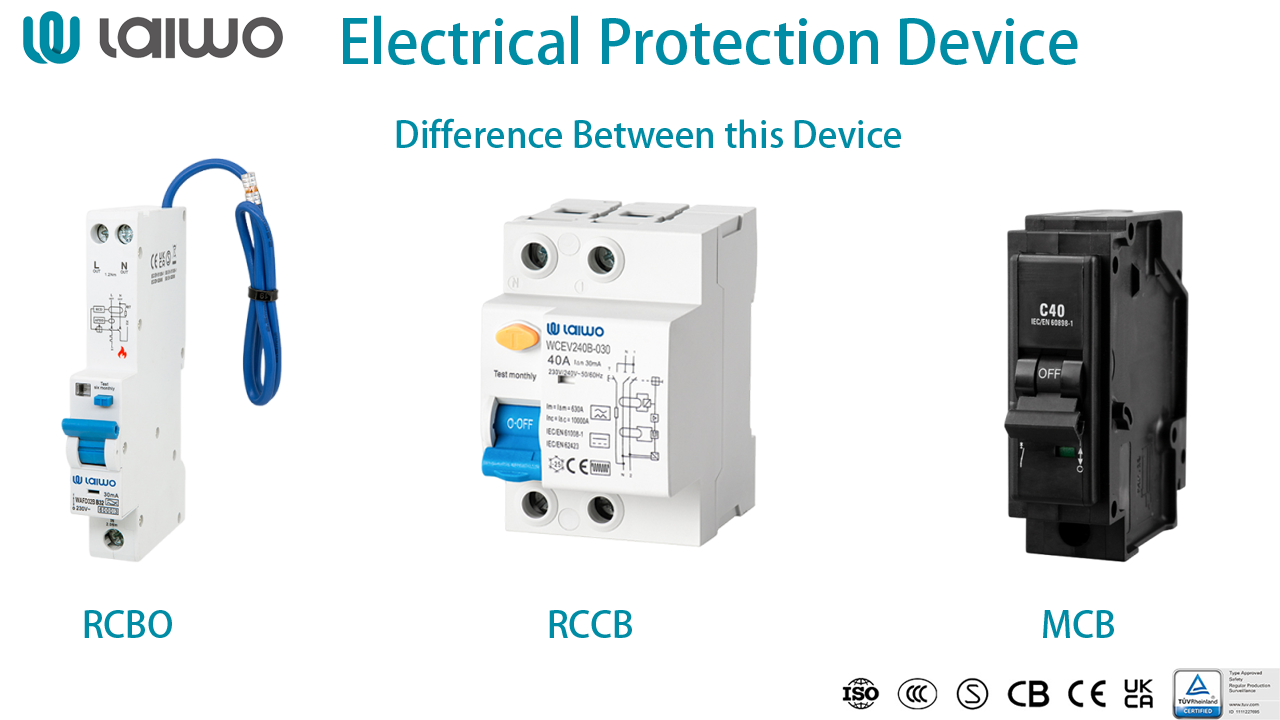
| Feature | MCB | RCCB | RCBO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Miniature Circuit Breaker |
Residual Current Circuit Breaker / Residual Current Device (RCD) / Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) |
Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection |
| Protection Against | Overload, Short Circuit | Earth Leakage (Electric Shock) | Overload, Short Circuit, Earth Leakage |
| Working Principle | Thermal (Overload), Magnetic (Short Circuit) | Kirchhoff's Current Law (Current Imbalance) | Combination of Thermal/Magnetic (Overcurrent) and Current Imbalance (Earth Leakage) |
| Primary Purpose | Equipment Protection | Personal Safety (Electric Shock Prevention) | Comprehensive Protection (Equipment and Personal Safety) |
| Resettable | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Typical Applications | General circuit protection in all settings | Wet areas, high-risk appliances, personnel protection focused areas | Individual circuit protection in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, high-risk circuits |
A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by excess current, typically resulting from an overload or a short circuit . Functioning as a safety accessory with an electro-mechanical mechanism, an MCB automatically interrupts the electrical circuit during such abnormal conditions, thereby preventing damage to the wiring and connected equipment while ensuring overall safety .
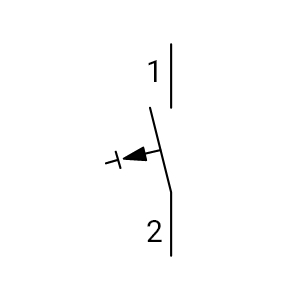
Symbol: A rectangle with a horizontal break, representing the interruption point

Learn More:
MCBs Guide: Types, Functions & Electrical Safety Tips
Miniature Circuit Breaker Symbols in Electrical Diagrams
A Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection (RCBO) is a sophisticated electrical safety device that integrates the functionalities of both an RCCB and an MCB into a single compact unit . This combination allows an RCBO to provide comprehensive protection against a wide range of electrical faults, including earth fault currents, short circuits, and overloading . By combining these two essential protective functions, RCBOs offer both personal safety by preventing electric shock through earth fault detection and equipment protection by interrupting overcurrents that could damage wiring and appliances . The integration of these features into a single device makes RCBOs a convenient and space-saving solution for electrical installations, simplifying the design and reducing the number of components required in an electrical panel.
Learn More: RCBO Ultimate Guide
A Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB), also commonly referred to as a Residual Current Device (RCD) or a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI), is a vital electrical safety device designed to detect current leakages, also known as earth faults, within an electrical circuit . The primary purpose of an RCCB is to prevent electric shock to humans by rapidly interrupting the electricity supply when it detects even a small leakage of current to earth .
Symbol: a rectangle with a test button symbol inside.
Learn More: RCCB Gudie
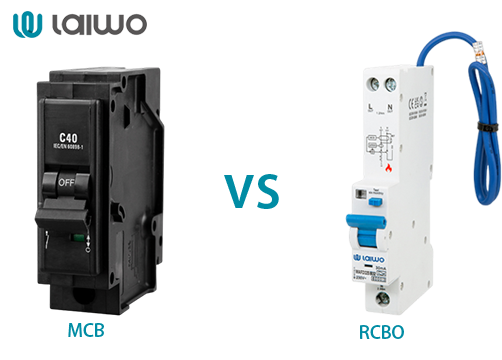
Protection Scope:
MCB: Protects only against overloads and short circuits (thermal-magnetic tripping).
RCBO: Protects against overloads, short circuits, and earth leakage faults (combines MCB and RCCB functions).
Primary Purpose:
MCB: Focuses on equipment protection.
RCBO: Provides comprehensive protection for both equipment and personal safety.
Cost and Complexity:
MCB: Simpler and cheaper.
RCBO: More expensive due to integrated protection features.
Both devices use thermal-magnetic tripping for overcurrent protection (overload and short circuits).
Both are resettable and serve as circuit interruption devices.
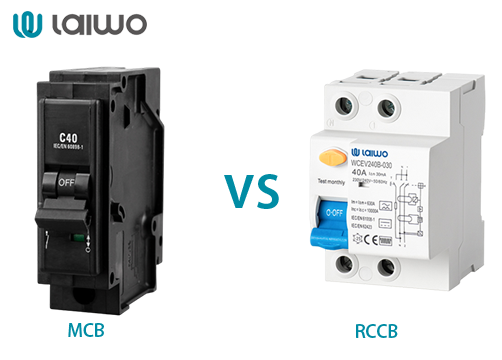
Protection Scope:
MCB: Detects overcurrents (overload/short circuit).
RCCB: Detects earth leakage currents (current imbalance between live and neutral).
Primary Purpose:
MCB: Prevents equipment damage.
RCCB: Prevents electric shock.
Response Mechanism:
MCB: Relies on thermal (bimetallic strip) and magnetic (solenoid) tripping.
RCCB: Uses a core balance transformer to detect current imbalance.
Both are resettable and act as safety devices in electrical systems.
Neither device alone provides comprehensive protection (MCB lacks earth fault detection; RCCB lacks overcurrent protection).
Protection Scope:
RCBO: Covers overloads, short circuits, and earth leakage.
RCCB: Only detects earth leakage faults.
Functionality:
RCBO: Integrates MCB and RCCB into a single unit.
RCCB: Requires a separate MCB for overcurrent protection.
Applications:
RCBO: Used for individual circuit protection to isolate faults.
RCCB: Typically installed for entire circuits in high-risk areas (e.g., bathrooms).
Both devices detect earth leakage faults using a core balance transformer.
Both include a test button to verify functionality.
In summary, Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs), Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCBs), and Residual Current Circuit Breakers with Overcurrent Protection (RCBOs) are all critical safety devices in modern electrical installations, each designed with specific functionalities to protect against different types of electrical faults.
Now that you have learnt about the various protective devices that can protect your electrical system, it is time to look for the one that best meets your requirements. When investing in electrical protection devices such as MCBs, RCCBs or RCBOs, make sure that you always get help from a reliable manufacturer/supplier such as laiwo. laiwo electrical is a one-stop solution for all your electrical needs including surge protectors, distribution boxes, earth leakage protection devices and switched sockets. If you have further questions or need assistance, please feel free to contact the Customer Service team.
Q1: Which is better, RCBO or MCB?
Ans: RCBO: Offers both overcurrent protection and protection against electric shock hazards due to ground faults, making it more comprehensive in terms of safety. MCB: Provides protection against overcurrents only and does not protect against electric shock hazards directly.
Q2: Which is better, RCBO or RCCB?
Ans: An RCCB is a simpler device that provides leakage current protection, while an RCBO is a more advanced device that provides both leakage current and overcurrent protection.
Q3: What is the disadvantage of a RCBO?
Ans: One potential disadvantage of RCBOs is their higher cost compared to standalone MCBs or RCDs.
Q4: Does RCCB trip on overload?
Ans: No, a Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) does not trip on overload; it's designed to detect and respond to leakage currents (earth faults) and not overloads or short circuits.
Q5: Can we use RCCB without MCB?
Ans: For circuits that supply power to high-risk areas, such as outdoor circuits, kitchens, and bathrooms, it is crucial to use both MCB and RCCB.
INQUIRY NOW