
In modern electrical systems, circuit breakers play a crucial role as protective elements. They not only prevent electrical equipment from overloading but also quickly cut off the power supply in case of a short circuit, ensuring the safety of personnel and the integrity of the equipment. However, there are various types of circuit breakers with different pole numbers on the market, from 1 pole to 4 poles, each with specific application scenarios and functional characteristics. This article will delve into the working principles, key differences, and application scenarios of 1-4 pole circuit breakers, particularly focusing on the critical question of when to choose a 4-pole circuit breaker instead of a 3-pole one. This will help readers fully understand the considerations for selecting circuit breakers.
A circuit breaker is a device used to protect electrical circuits from overloading, short circuits, or other faults. It can automatically detect abnormal current conditions and quickly cut off the power supply, preventing equipment damage or electric shock accidents. Essentially, a circuit breaker is an intelligent switch that can automatically close and protect the circuit when it detects a problem.
Learn More: MCBs Guide: Types, Functions & Electrical Safety Tips
The number of poles in a circuit breaker refers to the number of independent circuits or conductors it can control. Each “pole” represents an independent switching contact that can control a circuit wire and cut off the current. Depending on the number of wires it controls and the application scenario, circuit breakers can be divided into 1-pole, 2-pole, 3-pole, and 4-pole types.
From a professional perspective, the “pole” in a circuit breaker refers to the knife pole used for breaking the wire, but it does not necessarily… Design engineers are advised to collect and save this information!
A 1-pole circuit breaker is designed to control a single conductor in an electrical circuit. It is typically used in applications where only one wire needs to be switched or protected, such as in simple lighting circuits or individual appliance controls. The simplicity of 1-pole breakers makes them cost-effective and straightforward to install, but they lack the ability to provide coordinated protection across multiple conductors.
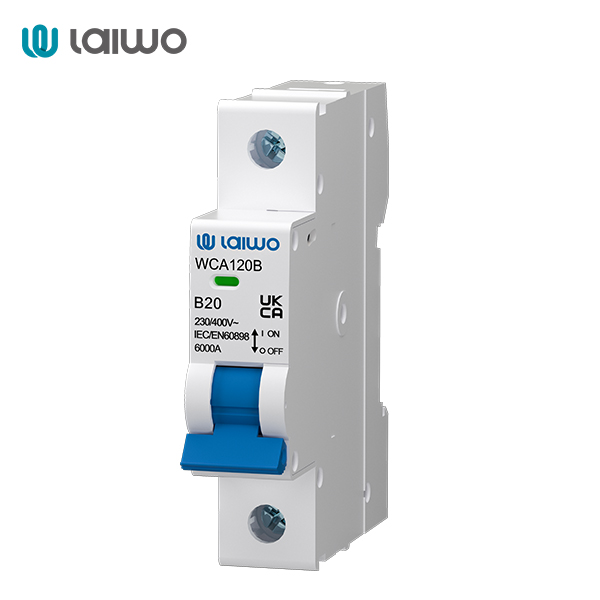


Learn More: Circuit Breaker Symbols in Electrical Diagrams
2-pole circuit breakers are designed to control two conductors simultaneously. They are commonly used in applications involving alternating current (AC) power, where both the live and neutral wires need to be disconnected simultaneously to ensure complete power isolation. Examples include standard household appliances and lighting systems where AC power is used.
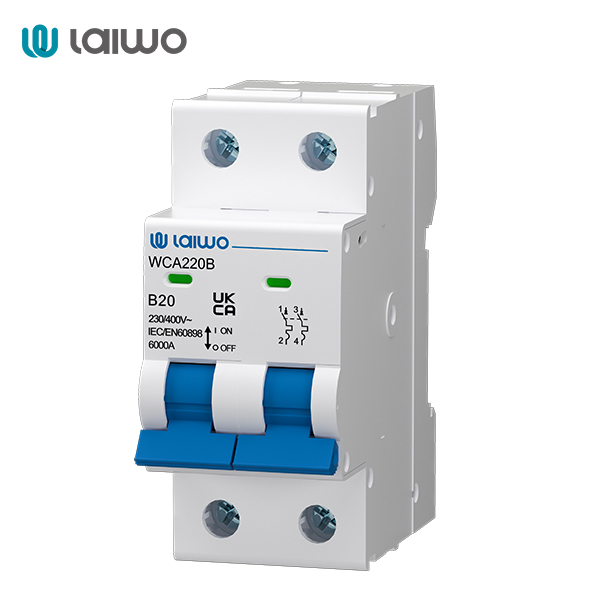

Learn More:
3-pole circuit breakers control three conductors, typically the three phase wires in a three-phase electrical system. They are essential in industrial and commercial settings where three-phase power is common, such as in motor control, industrial machinery, and large-scale lighting systems. 3-pole breakers provide balanced protection across all three phases, ensuring that if one phase fails, all phases are disconnected to prevent further damage.
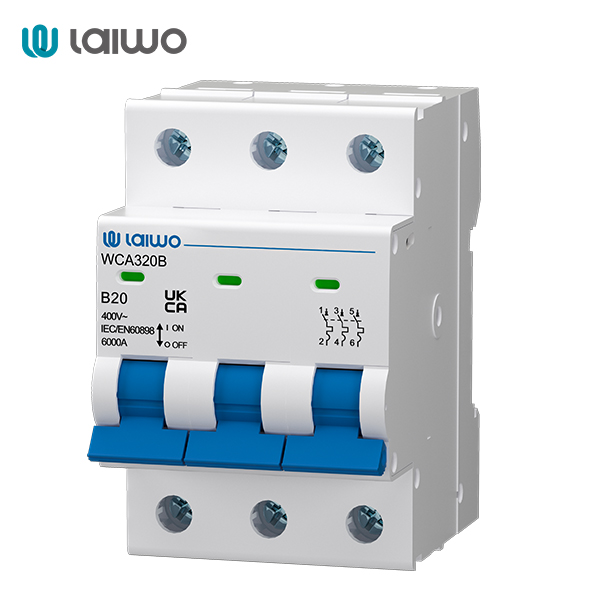

4-pole circuit breakers are designed to control four conductors. In addition to the three phase wires, they also include a neutral wire. This makes them particularly suitable for applications where the neutral wire needs to be separately controlled or protected, such as in certain types of industrial equipment, high-precision electronic devices, and systems where ground fault protection is required. 4-pole breakers offer enhanced safety and control in scenarios where the neutral wire plays a critical role.

When comparing 1-4 pole circuit breakers, several factors come into play:
Conductor Control: The number of conductors that can be controlled simultaneously increases with the number of poles.
Protection Capability: Higher pole numbers offer more comprehensive protection, especially in systems where multiple conductors need coordinated protection.
Installation Complexity: As the number of poles increases, so does the complexity and cost of installation.
Application Specificity: Each pole number is suited to specific types of applications, from simple single-wire controls to complex multi-phase systems.
Simple lighting circuits
Individual appliance controls
Low-voltage applications where only one wire needs protection
Applications where space is limited and a compact breaker is required
Standard household appliances
Lighting systems using AC power
Applications where both live and neutral wires need simultaneous disconnection
Simple motor controls
Industrial and commercial settings with three-phase power
Motor control centers
Large-scale lighting systems
Applications requiring balanced protection across three phases
Industrial equipment requiring separate control of the neutral wire
High-precision electronic devices
Systems where ground fault protection is critical
Applications involving four-wire systems, such as certain types of power distribution
Neutral Wire Control: If the application requires separate control or protection of the neutral wire, a 4-pole breaker is necessary.
System Requirements: Systems that operate on a four-wire configuration, such as those requiring ground fault protection, benefit from 4-pole breakers.
Safety Concerns: In environments where enhanced safety is paramount, especially those with high-risk operations, 4-pole breakers provide an additional layer of protection.
Regulatory Compliance: Certain industries or regions may have specific regulations that mandate the use of 4-pole breakers for particular applications.
Industrial Automation: In automated manufacturing lines, where precise control over power distribution is crucial, 4-pole breakers ensure that all conductors are properly managed.
Data Centers: High-precision electronic equipment in data centers often requires separate control of the neutral wire to prevent data loss or system failures.
Medical Equipment: Critical medical devices that cannot afford any power disruptions or malfunctions benefit from the enhanced control and protection offered by 4-pole breakers.
High-Voltage Applications: In high-voltage systems, the additional pole provides an extra safety measure, ensuring that all potential paths for current are properly in case of a fault.
Enhanced Protection: By controlling all four conductors, 4-pole breakers provide more comprehensive protection against overloads and short circuits.
Improved Safety: The ability to separately control the neutral wire reduces the risk of electrical hazards and enhances overall system safety.
Better Control: Fine-grained control over each conductor allows for more precise management of power distribution and usage.
Compliance with Standards: Many modern electrical systems and standards require 4-pole breakers for certain applications to meet safety and performance criteria.
Learn More:
20 Amp Breaker: Replacement & Wattage Guide
When do we use a 4 poles circuit breaker instead of a 3 poles circuit breaker?

Laiwo electrical is a one-stop solution for all your electrical needs including mcb, rcbo ,distribution boxes, surge protectors, earth leakage protection devices and dc products. If you have additional questions or need assistance, please feel free to contact the customer service team. Give us a call and we'll have a team of professionals answer your questions!
INQUIRY NOW