Next: RCBO Ultimate Guide

Electrical safety in residential and commercial installations is paramount, and one of the key devices ensuring that safety is the Residual Current Circuit Breaker(RCCB). In this guide, we’ll explore what an RCCB is, its uses, the advantages and disadvantages it brings, how it works, and the specific functions it performs.
The RCCB(full form in electrical: Residual Current Circuit Breaker), also commonly referred to as a circuit breaker, is an electrical safety device designed with the primary purpose of immediately interrupting the electricity supply upon detecting any leakage of current that could potentially lead to an electric shock. This rapid disconnection is crucial in minimizing the duration of exposure to hazardous electrical currents, thereby significantly reducing the risk of injury or even fatality. You might also encounter RCCBs being referred to as Residual Current Devices (RCDs) or Residual Current Breakers (RCBs), all denoting the same essential safety component.
Learn More: Understanding the difference between MCB RCCB and RCBO
Essentially, an RCCB functions as a specific type of Earth-leakage circuit breaker, engineered to identify and respond to imbalances in electrical circuits that indicate a leakage to earth. In a typical electrical setup, the RCCB is usually located within the distribution board (DB box) or the circuit breaker box of a building. A distinguishing feature that helps in identifying an RCCB is the presence of a 'Test' button on its face. This button allows for periodic verification of the device's operational readiness, ensuring it will function effectively when needed.

RCCB Symbol: a rectangle with a test button symbol inside.
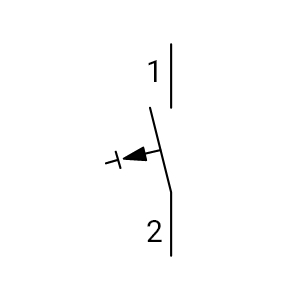
Learn More: Miniature Circuit Breaker Symbols in Electrical Diagrams
The primary purpose of an RCCB is to enhance electrical safety. It is used to:
Protect Against Electric Shock: By detecting leakage currents, the device can cut off the electrical supply almost instantly, reducing the risk of severe electrical shocks.
Prevent Fire Hazards: Electrical leaks or faults can sometimes result in overheating or sparks. RCCBs help prevent these conditions from escalating into fires.
Safeguard Electrical Equipment: By isolating the circuit in the event of an abnormal current flow, RCCBs also help protect sensitive electrical devices and systems from damage.
Because of these functions, RCCBs are often found in both domestic and industrial settings, where they serve as an essential part of the overall safety strategy.
1. Enhanced Personal Safety
Instant circuit disconnection upon detecting residual current, minimizing electric shock risks.
Critical for protecting users from live wire contact (e.g., homes, workplaces).
2. Fire Prevention
Detects leakage currents that cause overheating, reducing electrical fire hazards.
Isolates faulty circuits before flammable materials ignite.
3. Equipment Protection
Prevents appliance damage from faulty currents (e.g., short circuits, surges).
Extends device lifespan, lowering repair/replacement costs.
4. Versatile Application
Suitable for residential, industrial, and commercial settings, including older buildings.
Functions without direct earth wiring, ideal for outdated infrastructure.
5. Early Hazard Detection
Triggers alerts for minor current imbalances, enabling proactive repairs.
Prevents small faults from escalating into major hazards.
6. User-Friendly Features
Test button for quick functionality checks.
Advanced models include transient voltage filters to protect sensitive electronics.
1. No Overload/Short-Circuit Protection
Requires pairing with MCBs or RCBOs for full protection.
Only detects residual current leaks, not excessive current flow.
2. Live-Neutral Contact Risk
Fails to trip if a person touches both live and neutral wires (no earth leakage).
Critical gap in direct contact shock prevention.
3. Nuisance Tripping
Triggers falsely due to:
Sudden load changes (e.g., older appliances).
Normal leakage currents in devices like LED drivers.
4. Load Compatibility Issues
Struggles with non-standard waveforms (e.g., inverters, VFDs).
May trip falsely with filter-equipped power supplies.
5. Higher Costs
Pricier than basic MCBs due to advanced safety features.
Budget constraints in large-scale installations.
6. Limited Breaking Capacity
Lower fault current handling vs. MCBs (e.g., industrial short circuits).
Requires supplemental breakers for high-demand settings.
7. Environmental Sensitivity
Performance degrades under extreme temperatures or high humidity.
Requires strict adherence to manufacturer installation guidelines.
8. No Overheating Protection
Does not detect loose terminal connections causing heat buildup.
Relies on proper installation quality for this risk.
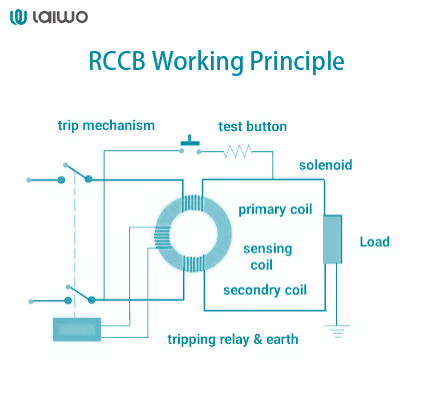
1. Current Transformer (Toroidal Coil)
Monitors live and neutral wires simultaneously.
Balanced currents: Magnetic fields cancel out → no residual flux.
Imbalanced currents (e.g., leakage): Creates net magnetic flux in the core.
2. Tripping Mechanism
Secondary winding detects flux-induced current.
Triggers solenoid/relay if current exceeds sensitivity rating (e.g., 30mA).
Instantly opens contacts to cut power (<30 milliseconds).
3. Test Button Circuit
Simulates earth fault by diverting a small current.
Includes safety resistor to limit test current.
Validates RCCB’s responsiveness when pressed.
4. Reset Mechanism
Restores power post-trip after fault resolution.
Manual switch/button ensures user control.
5. Key Workflow
Normal Operation: Live/neutral currents balanced → no tripping.
Fault Detection: Leakage current → flux imbalance → secondary current.
Instant Disconnection: Trip mechanism activates → circuit breaks.
1. Residential Safety
Electric shock prevention: Critical in moisture-prone areas (bathrooms, kitchens) with faulty wiring/appliances.
Fire risk reduction: Detects hidden leakage currents in wiring before overheating occurs.
24/7 monitoring: Essential for homes with high-risk zones (e.g., outdoor outlets, pools).
2. Commercial Protection
Personnel & equipment safety: Safeguards offices, malls, and public spaces from electrical faults.
Downtime prevention: Minimizes disruptions to business operations by isolating faults swiftly.
Regulatory compliance: Meets mandatory safety standards for commercial electrical systems.
3. Industrial Reliability
Worker safety: Protects against shocks in high-voltage environments (factories, plants).
Machinery protection: Detects imbalances caused by heavy industrial equipment (e.g., motors, CNC machines).
Hazard mitigation: Critical in wet/hazardous zones (processing units, chemical storage).
| Type | Detected | Application |
| Type AC | Detects sinusoidal AC residual currents | General residential circuits (traditional appliances) |
| Type A | Detects AC + pulsating DC currents | Electronics-heavy setups (home offices, EV chargers) |
| Type B | Detects AC, pulsating DC, and smooth DC currents | Industrial machinery, solar/wind systems |
| Type F | Handles mixed AC/DC currents with anti-nuisance tripping | HVAC systems, variable-speed drives |
| Type H | Ultra-high sensitivity for critical safety | Hospitals, laboratories |
| Pole | System | Application |
| 2-Pole RCCBs | For single-phase systems (1 live + 1 neutral) | Common in homes/small businesses |
| 4-Pole RCCBs | For three-phase systems (3 live + 1 neutral) | Used in factories/large commercial setups |
| Sensitivity | Application |
| 10mA/30mA | Direct contact protection (bathrooms, schools). |
| 100mA/300mA | Fire prevention & indirect contact safety (main panels) |
| 500mA/1000mA | Heavy industrial equipment protection |
| Current Rating | Application |
| 16A–63A | Residential/commercial circuits (lighting, outlets) |
| 80A–100A+ | Industrial machinery, high-load systems |
Now that you have learnt about the RCCB that can protect your electrical system, it is time to look for the one that best meets your requirements. When investing in electrical protection devices such as MCBs, RCCBs or RCBOs, make sure that you always get help from a reliable manufacturer/supplier such as laiwo. laiwo electrical is a one-stop solution for all your electrical needs including surge protectors, distribution boxes, earth leakage protection devices and switched sockets. If you have additional questions or need assistance, please feel free to contact the customer service team. Give us a call and we'll have a team of professionals answer your questions!
Q1: What are the Differences between RCBOs and RCCBs?
Ans:
Protection Scope:
RCBO: Covers overloads, short circuits, and earth leakage.
RCCB: Only detects earth leakage faults.
Q2: What are the Differences between MCBs and RCCBs?
Ans:
Protection Scope:
MCB: Detects overcurrents (overload/short circuit).
RCCB: Detects earth leakage currents (current imbalance between live and neutral).
Next: RCBO Ultimate Guide
INQUIRY NOW