Next: AC vs DC MCBs: How to Choose the Right Circuit Breaker

In modern electrical systems, protecting electrical circuits from hazards like overloads and short circuits is non-negotiable. At the heart of this protection lies the miniature circuit breaker (MCB), a critical protective device that disconnects the circuit during faults. Whether you’re an electrician, homeowner, or tech enthusiast, understanding how MCBs work, their tripping curve, and types of MCBs is essential for ensuring the safety of your electrical appliances and infrastructure. This guide dives deep into MCB fundamentals, applications, and best practices.

MCB stands for Miniature Circuit Breaker. It’s an automatic switch designed to handle abnormal currents caused by overload or short circuits. Unlike traditional fuses, MCBs are reusable—simply reset them after they trip. Key features include:
Breaking Capacity: The maximum current an MCB can interrupt safely.
Trip Characteristics: Determined by its tripping curve (e.g., Type B MCB for residential use).
Number of Poles: Single-pole (1P) for basic circuits, triple-pole (3P) for high-power systems.
1 Pole MCB Symbol
A rectangle with a horizontal break, representing the interruption point

Learn More: Miniature Circuit Breaker Symbols in Electrical Diagrams
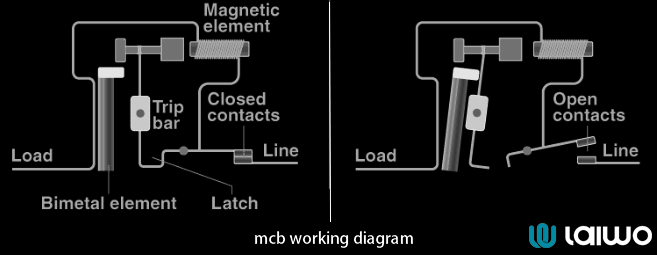
When an electrical load exceeds the MCB’s rating, it disconnects the circuit via two mechanisms:
Thermal Trip: A bimetallic strip bends under excessive heat (from overloads), triggering a trip.
Magnetic Trip: A solenoid reacts instantly to short circuits, cutting off power within milliseconds.
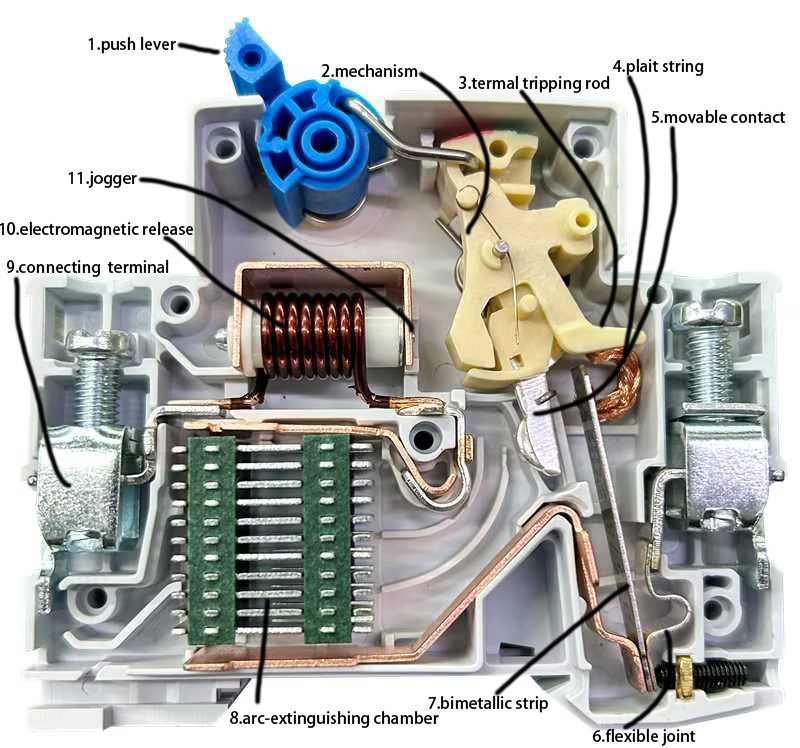
1. push lever
2. mechanism
3. termal tripping rod
4. plait string
5. movable contact
6. flexible joint
7. bimetallic strip
8. arc-extinguishing chamber
9. connecting terminal
10. electromagnetic release
11. jogger
MCBs are classified by their tripping curve, which defines their response time:
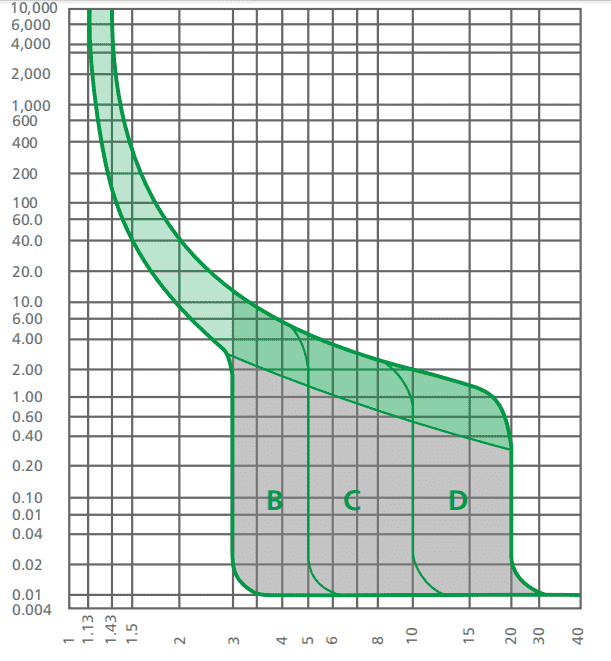
| MCB Type | Trip Curve | Sensitivity | Common Applications | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type B | Trip at 3-5× rated current | High | Residential lighting, sockets | Homes, offices |
| Type C | Trip at 5-10× rated current | Moderate | Motors, HVAC systems | Commercial buildings, industrial gear |
| Type D | Trip at 10-20× rated current | Low | Heavy machinery, transformers | Factories, welding equipment |

Single-Pole (1P): Protects one live wire. Common in lighting circuits.
Double-Pole (2P): Safeguards live and neutral wires. Used for power supply to outlets.
Three-Pole (3P): For three-phase systems in factories or high-power setups.
6A to 32A MCB: For residential circuits (e.g., a 32A MCB load capacity suits kitchen appliances).
63A to 125A: Industrial machinery and solar panels.
While MCBs handle lower currents, MCCBs (Molded Case Circuit Breakers) manage higher capacities (up to 2500A). MCCB and MCB difference lies in scalability—never replace MCCB with MCB in industrial settings.
.png)
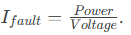
Determine the circuit’s maximum current. For example:
A 32A circuit requires a 32A MCB.
Add a 20% buffer for startup surges (e.g., 10A load → 12A MCB).
Type B: Homes with electronics (low surge).
Type C: HVAC systems or motors (moderate surge).
Type D: Heavy machinery (extreme surge).
Ensure the MCB’s breaking capacity exceeds the circuit’s potential fault current.
Learn More: AC vs DC MCBs: How to Choose the Right Circuit Breaker
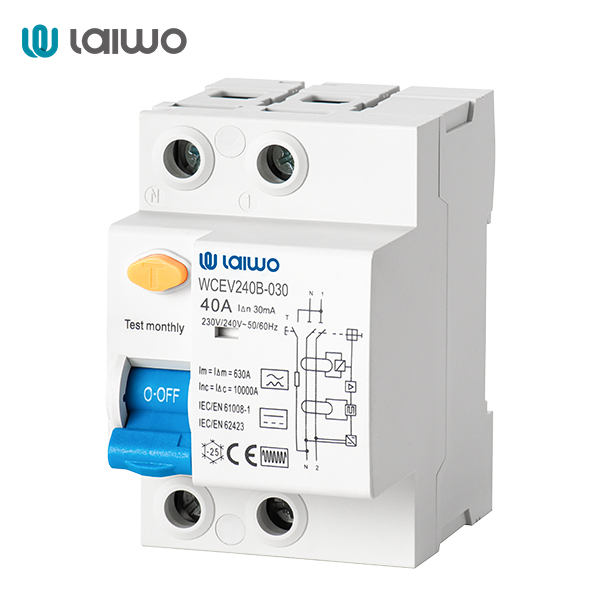

| MCB name | WCEV Type B DC Mini Circuit Breaker |
| Rated Current | 25A/40A/63A |
| Rated voltage Un | 230/400V AC |
| Rated frequency | 50HZ |
| Peak withstand current | 3kA |
| Brand | laiwo |
| Whatsapp/Tel | +86-15067706272 |
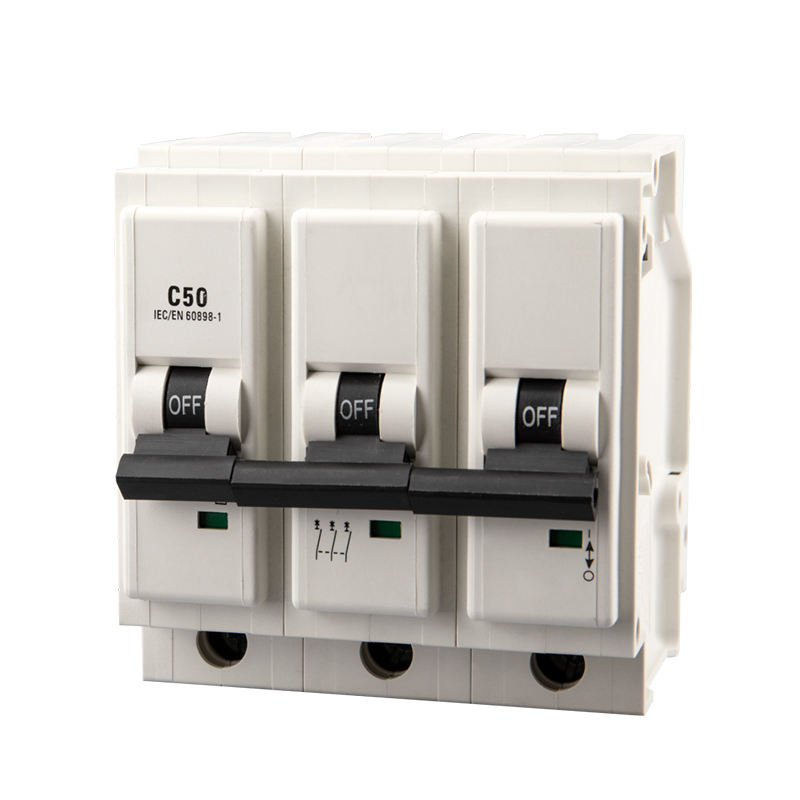

| MCB name | WCP Miniature Circuit Breakers plug in MCB |
| Rated current In (A) | 6/10/16/20/25/32/40 |
| Number of Poles | 1P/2P/3P/4P |
| Rated breaking capacity(A) | 6KA |
| Thermo-magnetic release characteristic | B/C/D |
| Brand | laiwo |
| Whatsapp/Tel | +86-15067706272 |
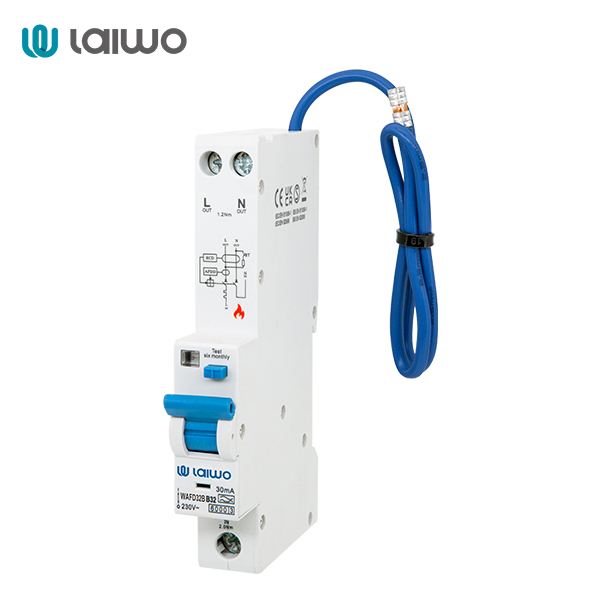

| MCB name | WAFD Type A/AC micro circuit breaker |
| Rated voltage(Ue) | AC230V |
| Rated current(In) | 6A/10A/16A/20A/25A/32A/40A |
| Number of N poles | 1P+N |
| Protection Curve | B |
| Brand | laiwo |
| Whatsapp/Tel | +86-15067706272 |
INQUIRY NOW