Next: Double 16A MCB: Prevent Overloads & Short Circuits (With Market Analysis)

Early electrical systems relied on fuses—single-use wires that melted during faults. Today’s miniature circuit breakers mcbs are reusable, smarter, and faster. Innovations like adjustable trip characteristics and IoT-enabled MCBs are reshaping safety standards.
In this guide, we’ll decode the mcb full form in electrical, explore its working principles, and explain why it’s a non-negotiable protective device in modern homes.

MCB stands for Miniature Circuit Breaker. Think of it as a smart switch that automatically turns off when your electrical system faces trouble. Unlike old-school fuses, MCBs don’t need replacing after tripping—just flip the switch back on once the issue is fixed.
The full form of MCB reveals its purpose: Miniature Circuit Breaker. “Miniature” refers to its compact size, while “circuit breaker” highlights its role in breaking the circuit during faults.
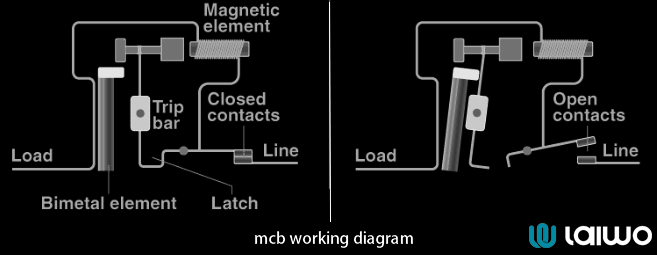
The mcb working principle revolves around two main threats: overloads and short circuits.
When too many appliances run simultaneously, wires overheat. The MCB detects this excess current using a bimetallic strip. Heat bends the strip, triggering the trip characteristics to break the circuit.
A short circuit is like a highway pileup—electricity takes a dangerous shortcut. The MCB’s electromagnetic coil reacts instantly, disconnecting power within milliseconds to prevent fires or damage caused by overloading or short circuits.
| Feature | MCB | MCCB |
| Current Range | Up to 125A | Up to 2,500A |
| Breaking Capacity | Lower (6KA-10KA) | Higher(10KA-100KA) |
| Application | Homrs/Small Offices/Factories | Factories/Large Industries |
While both are types of circuit breakers, MCCBs handle heavier loads. MCBs are the compact, everyday heroes; MCCBs are their industrial cousins.
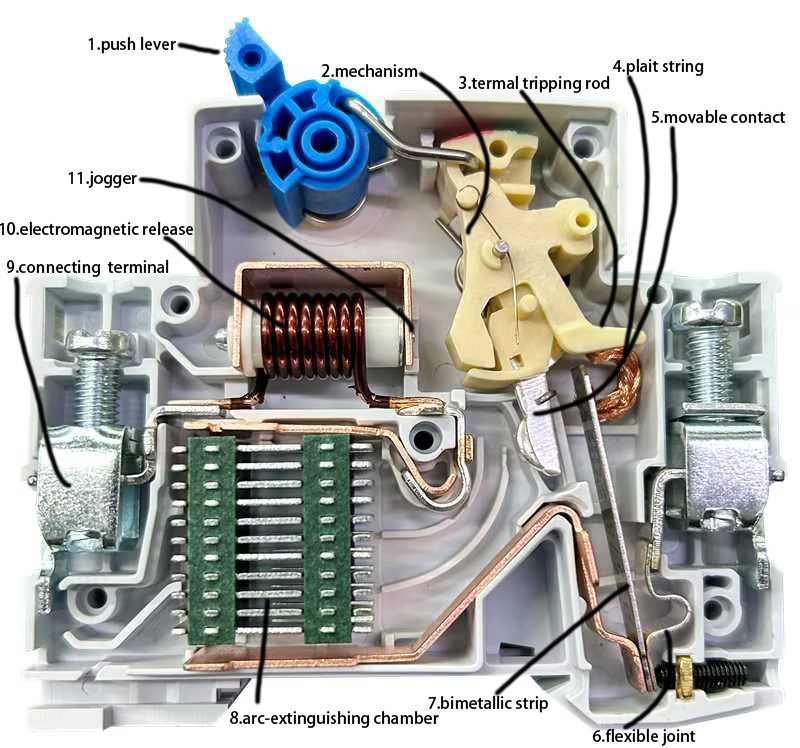
Terminals: Where wires connect.
Bimetallic Strip: Detects overloads.
Electromagnet: Reacts to short circuits.
Trip Mechanism: The “off switch” triggered by faults.
Preventing Damage to wiring and appliances.
Earth Fault Detection: Some advanced MCBs combine with ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) to detect current leaks.
Residential Safety: Found in distribution boards of homes.
Commercial Use: Protects electrical appliances in offices.
Industrial Backup: Works alongside MCCBs for layered safety.

| Type | Application |
| Type A MCB | Medical devices / Servers / Residential |
| Type B MCB | Residential |
| Type C MCB | Commercial |
| Type D MCB | Industrial |
Check the Load: Match the mcb rating to your appliance’s current (e.g., 16A for ACs).
Understand Trip Curves: Type B for homes, Type C for motors.
Prioritize Breaking Capacity: Ensure it can handle your area’s fault current.
Look for Certifications: IEC 60898 for household MCBs.
Click on this blog(MCB Types Fully Explained: A Guide to Choosing from Type A to Type D) for more detailed information
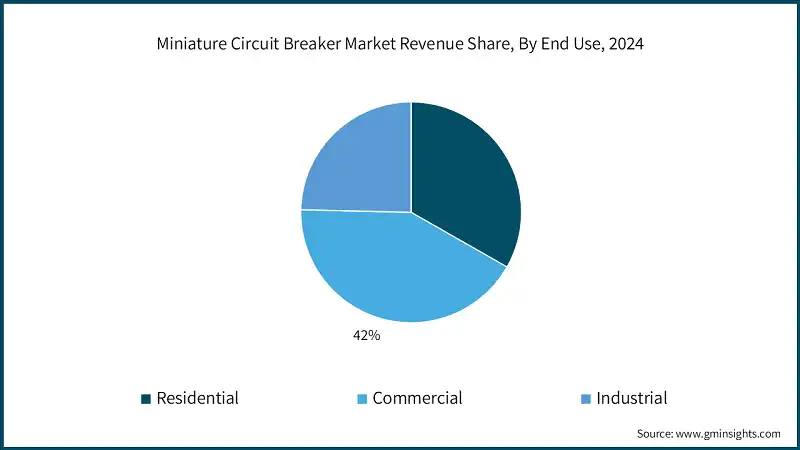
Source:gminsights
Understanding mcb market needs: household electricity systems, business infrastructure installations, and heavy-duty industrial power networks.
Cost-Value Optimization: Leverage cost-efficient mcb suppliers in China/SE Asia (e.g., China’s $1.5B 2023 grid upgrade).
Multi-Regional Certifications: Ensure that mcb products comply with CCC, CE, UKCA, TUV, CB, SEMKO, ISO9001, etc.
Supplier Evaluation Criteria: Ensure production stability, customised requirements and fast after-sales support.
Click here to get today's daily quote for laiwo mcb.
A: It’s a rectangle with a switch-like line inside, often labeled “MCB.”
A: It could signal overloading, faulty appliances, or a short circuit.
A: Standard MCBs don’t. For that, you’ll need an ELCB or RCCB.
A: Common ratings include 6A, 16A, 32A, etc. Choose based on your circuit’s needs.
A: We offer a professional catalogue with detailed technical specifications.
Whether you’re a Individual Buyers or a B2B Procurement Personnel,by understanding miniature circuit breaker working principles, types, and applications,empowers you to select right product and mcb manufacturer.
INQUIRY NOW